The Operator Role in Venture Studios
Transforming Concepts into Companies
The operator function represents the distinctive execution engine of venture studios, transforming validated concepts into functioning businesses with repeatable efficiency. While traditional venture capital provides capital and advisory support, venture studios actively build and operationalize new companies through hands-on execution. This article introduces a comprehensive framework for understanding and evaluating the operator role within venture studios, providing investors with concrete metrics to assess operational effectiveness. By recognizing that successful venture studios systematize company building through developed playbooks, shared resources, and process optimization, investors can better identify studios that consistently translate entrepreneurial vision into market-ready entities with superior capital efficiency and accelerated time-to-market.
The Execution Engine of Venture Creation
The operator role stands as the defining characteristic that separates venture studios from other early-stage investment vehicles. While accelerators offer guidance and venture capital firms provide oversight, venture studios actively execute on company building. As defined in our core framework, the operator role is "responsible for executing the company's plan for product development, going to market, and other early-stage activities to establish traction." This hands-on approach fundamentally distinguishes the venture studio model.
Instead of merely advising entrepreneurs, venture studios deploy resources, build systems, and implement operational frameworks that transform concepts into functioning businesses. They don't simply suggest paths forward—they build the paths themselves, constructing the operational foundation upon which portfolio companies can scale.
For investors evaluating venture studios, understanding this operational capacity is critical. The operator function directly impacts key performance metrics including time-to-market, capital efficiency, and company survival rates. It represents the engine that converts entrepreneurial vision into tangible business outcomes with systematic discipline.
The Operational Advantage: Why Studios Outperform
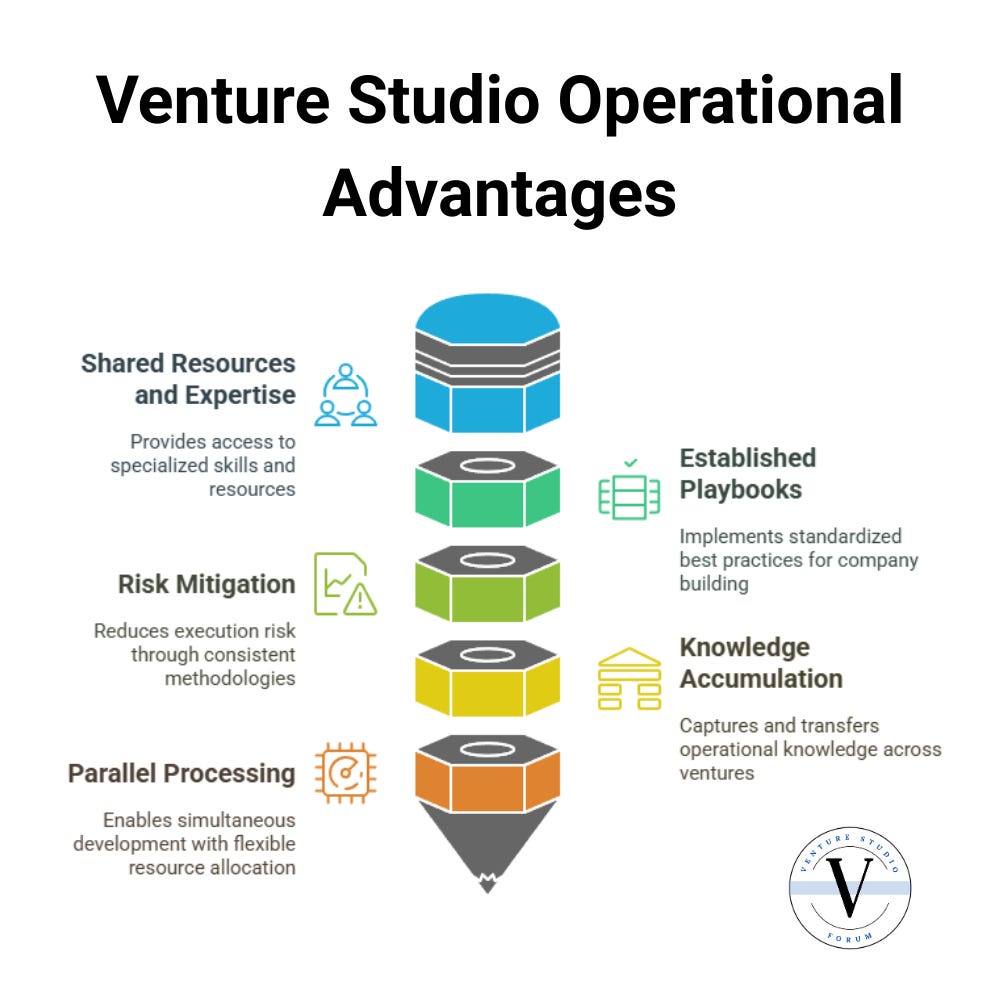
Research indicates that venture studios substantially outperform traditional startup approaches on key operational metrics. According to the Global Startup Studio Network, studio-created startups reach Series A funding in approximately 25 months from inception, compared to 56 months for traditional startups. This accelerated timeline derives from several structural advantages in the operator function:
1. Shared Resources and Specialized Expertise
Venture studios leverage economies of scale by distributing specialized operational resources across multiple portfolio companies. This enables access to expertise in product development, marketing, finance, and other functions that early-stage companies typically cannot afford individually.
2. Established Playbooks and Methodologies
Rather than reinventing operational processes for each new company, studios implement standardized playbooks that codify best practices for company building. These playbooks evolve continuously based on portfolio experience, creating compounding advantages over time.
3. Risk Mitigation Through Systematic Execution
By applying consistent operational methodologies, studios reduce execution risk in early-stage ventures. Operational issues that typically derail startups are anticipated and addressed through established processes and preventative measures.
4. Knowledge Accumulation and Transfer
Studios create mechanisms for capturing and transferring operational knowledge across portfolio companies. Lessons learned in earlier ventures directly benefit later companies, creating an institutional memory that individual startups cannot replicate.
5. Parallel Processing and Resource Flexibility
The studio model enables parallel development across multiple ventures with flexible resource allocation based on changing priorities and opportunities. This adaptability allows studios to optimize resource deployment as portfolio companies evolve.
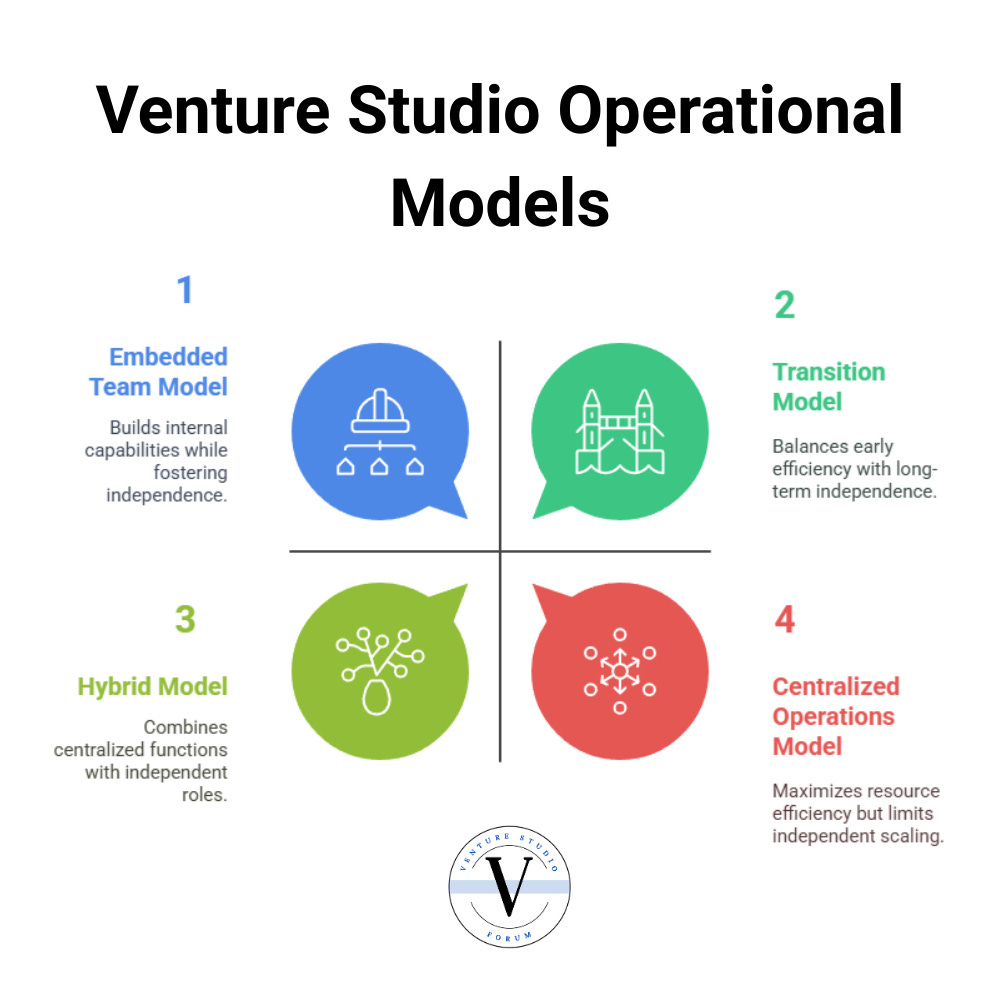
Operational Models: Diversity in Approach
While all venture studios provide operational support, the specific models vary considerably:
1. Centralized Operations Model
In this approach, most operational functions remain centralized within the studio, with portfolio companies receiving ongoing support throughout their development. This model maximizes resource efficiency and knowledge transfer but may create dependencies that slow independent scaling.
2. Transition Model
Studios employing this model provide intensive operational support during early stages, then systematically transition functions to the portfolio company as it matures. This approach balances early efficiency with long-term independence.
3. Embedded Team Model
Some studios deploy dedicated operational teams that embed within portfolio companies for defined periods. These teams implement studio methodologies while building the company's internal capabilities, eventually withdrawing as the company develops its own operational capacity.
4. Hybrid Model
Many studios employ a hybrid approach, keeping certain specialized functions (e.g., design, data science) centralized while transitioning core operational roles to portfolio companies. This balances efficiency with independence based on functional requirements.
When evaluating a venture studio's operator function, investors should consider which model best aligns with the studio's focus areas, company types, and stated objectives. The appropriateness of the operational model is often more important than adherence to any particular approach.
Common Functions of the Operator Role
The operator role encompasses several discrete functions, each requiring distinct capabilities and processes. Studio often concentrate on a handful of operator functions to own in house, partnering with founders and leveraging external resources to fill in any gaps. Owning the core operations that add the most value is the goal, rather than owning end to end operations.
Product Development Processes
Venture studios must establish efficient methodologies for translating validated concepts into functional products. This includes technical resource allocation, development frameworks, and quality assurance processes.
Key evaluation questions:
What formal product development methodologies does the studio employ?
How does the studio balance speed and quality in early product development?
What is the studio's track record in delivering minimum viable products on schedule?
How does the studio incorporate customer feedback into product development cycles?
Technical Resource Allocation
Effective studios develop systems for allocating technical talent and resources across portfolio companies based on prioritization frameworks, developmental stage, and market opportunity.
Key evaluation questions:
How does the studio determine resource allocation across portfolio companies?
What methods are used to ensure technical resources are deployed efficiently?
How are technical priorities established and managed across competing needs?
What is the ratio of dedicated versus shared technical resources across portfolio companies?
Go-to-Market Execution
Studios must implement standardized approaches to market entry, including customer acquisition strategies, pricing models, and distribution channel development.
Key evaluation questions:
What repeatable go-to-market frameworks has the studio developed?
How does the studio validate channel strategies before significant investment?
What metrics are used to evaluate early go-to-market effectiveness?
How are go-to-market learnings captured and applied across portfolio companies?
Team Building and Talent Deployment
A crucial operational function involves recruiting, deploying, and developing talent for portfolio companies, including both technical and business roles.
Key evaluation questions:
What is the studio's process for identifying talent needs for new ventures?
How does the studio attract and retain high-quality talent?
What frameworks exist for transitioning talent from studio to portfolio companies?
How are equity and incentive structures designed to align team member interests with company outcomes?
Operational Systems Development
Studios must build foundational business systems including financial management, legal structures, compliance frameworks, and administrative processes that enable portfolio companies to function effectively.
Key evaluation questions:
What standardized operational systems has the studio developed for new ventures?
How are these systems transferred to and implemented within portfolio companies?
What metrics are used to evaluate operational efficiency of portfolio companies?
How does the studio balance standardization with customization for specific company needs?
Knowledge Capture and Transfer
Effective studios implement systems for capturing operational learnings and transferring knowledge across portfolio companies, creating compounding advantages over time.
Key evaluation questions:
What formal knowledge management systems has the studio implemented?
How are operational learnings documented and shared?
What mechanisms ensure that portfolio companies benefit from earlier company experiences?
How does the studio measure the effectiveness of knowledge transfer activities?
The Complementary Nature of Studio and Founder Operations
A critical aspect often overlooked when evaluating venture studios is understanding how their operational capabilities are designed to complement—not replace—the founder's responsibilities. Rather than owning operations end-to-end, successful studios typically specialize in specific functional areas while creating clear expectations for what founders will own.
Most studios establish boundaries and interfaces between studio-provided operations and founder-led functions. This collaborative approach ensures both alignment and clarity on responsibilities throughout the company building process:
The most effective studios develop clear documentation of these operational boundaries and establish transition plans for gradually shifting responsibilities to the founding team. Rather than creating dependence, their goal is to accelerate early development and then steadily transfer operational ownership as the company matures.
When evaluating a venture studio's operator function, investors should examine not just what operations the studio provides, but how those functions integrate with and complement the expected founder contributions. The quality of this operational interface often determines whether a studio truly accelerates company development or creates problematic dependencies that hinder long-term success.
Evaluating Operational Effectiveness: Key Performance Indicators
Investors should assess the effectiveness of a venture studio's operator function using the following quantitative and qualitative metrics:
1. Time to MVP
The average time required to develop a minimum viable product from concept approval. This metric reflects the studio's ability to efficiently translate concepts into testable products.
2. Time to Market
The average time from concept approval to commercialization. This metric encompasses the full product development and go-to-market preparation cycle. Standards vary greatly by industry with deeptech and biotech time to market often becoming a post-spinout metric.
3. Time to Revenue
The average time from concept to first revenue. This critical metric reflects the studio's ability to build not just products but revenue-generating businesses.
4. Resource Efficiency
The operational cost per company built to revenue stage, including allocated studio resources. This metric reflects the capital efficiency of the studio's operational model.
5. Team Scalability Ratio
The number of portfolio companies effectively supported per studio team member. This metric indicates operational leverage and scalability of the studio model. This metric requires nuanced interpretation, as it reflects the studio's resourcing strategy rather than simply indicating efficiency. Many studios effectively leverage part-time experts and external partners, particularly in early stages, while dedicated studios often provide significantly more support hours per company than accelerators with similar ratios.
6. Knowledge Transfer Rate
The effectiveness of applying learnings across portfolio companies, measured through adoption rates of best practices and reduced time to operational milestones for newer companies.
7. Operational Milestone Achievement
The success rate at meeting defined operational goals across portfolio companies, including product development, customer acquisition, and revenue targets.
Reference Case: B2B SaaS Studio Operational Model
To illustrate how these KPIs apply in practice, consider a typical B2B SaaS-focused venture studio:
Studio-Owned Functions:
Technical development (engineering leadership, initial coding team)
Product design and UX
Initial marketing infrastructure
Financial modeling and metrics tracking
Fundraising preparation and investor relations
Founder-Owned Functions:
Product vision and roadmap priorities
Customer relationship development
Industry expertise application
Team culture and leadership
Long-term strategic direction
Typical Performance Metrics:
Time to MVP: 4-5 months
Time to Market: 7-8 months
Time to Revenue: 10-12 months
Resource Efficiency: $350,000-$450,000 per company to revenue
Team Scalability: 2.0 companies per full-time studio team member
Knowledge Transfer: 25% improvement in go-to-market efficiency for later companies
Milestone Achievement: 75% of defined milestones met on schedule
As the company progresses toward Seed funding, the studio gradually transitions technical leadership to a CTO hired into the portfolio company while maintaining support roles in specialized areas like growth marketing and financial planning. This handoff typically occurs over 6-9 months, with complete operational independence achieved 12 months post-formation.
Reference Case: B2B SaaS Studio Operational Model
To translate these abstract metrics into a practical context, let's examine how a typical B2B SaaS-focused venture studio operates. This example represents a composite of successful studios in this space and demonstrates how the operational role functions in practice.
Imagine "Catalyst Studio," which specializes in creating B2B SaaS companies targeting mid-market enterprise customers. Catalyst employs a team of 15 professionals, including engineers, designers, product managers, marketers, and finance specialists. The studio typically works with 6-8 portfolio companies at various stages simultaneously.
When Catalyst identifies a promising opportunity—for instance, a solution for streamlining compliance workflows in regulated industries—they first validate the concept through customer interviews and market analysis. Once validated, they bring in a founder with domain expertise who becomes the face and leader of the new venture.
The Operational Division of Labor:
Catalyst doesn't attempt to handle every operational aspect of the new company. Instead, they focus on areas where they have proven expertise and processes, while complementing the founder's industry knowledge and leadership:
Studio-Owned Functions:
Technical development (engineering leadership, initial coding team)
Product design and UX
Initial marketing infrastructure
Financial modeling and metrics tracking
Fundraising preparation and investor relations
Founder-Owned Functions:
Product vision and roadmap priorities
Customer relationship development
Industry expertise application
Team culture and leadership
Long-term strategic direction
This division creates a powerful symbiosis: the studio provides the operational infrastructure and execution capacity to move quickly, while the founder contributes the domain knowledge and customer relationships essential for product-market fit. Neither could achieve the same velocity alone.
Performance in Practice:
For a typical B2B SaaS company in Catalyst's portfolio, operational performance metrics consistently outpace industry averages:
Time to MVP: 4-5 months – Through reusable technical components and established design patterns, Catalyst delivers working products in less than half the time of typical startups.
Time to Market: 7-8 months – The studio's established go-to-market playbooks enable rapid customer onboarding and feedback collection.
Time to Revenue: 10-12 months – Leveraging both founder relationships and studio connections, new ventures typically secure initial paying customers within a year of concept approval.
Resource Efficiency: $350,000-$450,000 per company to revenue – By sharing resources across portfolio companies and applying proven processes, Catalyst achieves significantly greater capital efficiency than standalone startups.
Team Scalability: 2.0 companies per full-time studio team member – Through careful resource allocation and specialized roles that work across multiple portfolio companies, the studio maintains effective operations without diluting support quality.
Knowledge Transfer: 25% improvement in go-to-market efficiency for later companies – Each new portfolio company benefits from learnings captured from previous ventures, with systematic documentation of successful tactics and common pitfalls.
Milestone Achievement: 75% of defined milestones met on schedule – Through established project management practices and realistic planning, Catalyst's portfolio companies consistently hit development and growth targets.
The Evolution of Operational Support:
As portfolio companies mature, Catalyst's operational involvement evolves. When a company secures seed funding (typically 10-12 months post-formation), the studio transitions core functions to the company's own team.
The company gradually builds its own engineering team, typically starting with a CTO hired at the seed stage, while Catalyst maintains support in specialized areas like growth marketing and financial planning where fractional expertise remains valuable. By the time the company approaches Series A (typically 18-24 months in), the studio has been fully out of operational support role for 6-12 months and is primarily providing strategic advisory.
This gradual transition ensures that portfolio companies develop self-sufficiency without experiencing operational gaps. By the time they reach Series A, companies have developed their own operational capabilities while retaining access to the studio's knowledge base and specialized resources as needed.
This reference model illustrates how the operational metrics and frameworks discussed earlier translate into tangible company building in practice. While specific approaches vary across studios, this pattern of complementary capabilities, systematic execution, and graduated independence represents the operational role at its most effective.
Common Red Flags in the Operator Function
When evaluating venture studios, investors should be alert to these warning signs indicating potential weaknesses in the operator role:
1. Misalignment Between Track Record and Operations Scope
When a studio's operational team lacks demonstrated expertise in the domains where they claim to build companies. This increases the risk that the studio cannot effectively execute in their target markets.
2. Support Duration Misaligned with Company Type
Studios applying standardized operational timeframes regardless of company type. Deep tech companies typically require longer operational support (18-36 months) than software companies (9-18 months).
3. Inadequate Operating Budget
When a studio's operating budget is insufficient to support its stated company creation pace. Under-resourced operational teams lead to quality issues and missed timelines.
4. Team Size-Portfolio Imbalance
Studios supporting too many portfolio companies relative to their operational team size. This typically results in diluted support and underperformance across the portfolio.
5. Unrealistic Development Timelines
Studios consistently underestimating the time required to develop market-ready products and achieve operational milestones. This often indicates inexperience or overly optimistic planning.
6. Over or Under-reliance on External Resources
Studios that depend heavily on contractors or part-time resources rather than dedicated operational teams. While some external expertise is appropriate, over-dependence compromises knowledge accumulation and process consistency. The balance between internal and external resources requires careful evaluation. Strategic use of contractors can provide flexibility and specialized expertise, particularly for early-stage studios. However, studios that outsource all core operational functions may struggle to develop institutional knowledge. The key assessment is whether the studio maintains capabilities aligned with its value proposition while leveraging external resources appropriately.
7. Insufficient Process Documentation
Studios lacking comprehensive playbooks and operational documentation. Effective studios codify their operational knowledge into transferable frameworks and processes.
Evaluating the Operator Role in Venture Studios
The operator function represents the distinctive execution capability that separates venture studios from other early-stage investment models. By systematically building and operationalizing new companies, rather than merely advising existing ones, studios aim to create ventures with greater efficiency and higher success rates than traditional approaches.
For investors evaluating venture studios, assessing the operator role requires examining both the systems and the talent involved. High-performing studios demonstrate clear methodologies for product development, resource allocation, and go-to-market execution. They maintain operational discipline through established playbooks, implement effective knowledge management systems, and deploy appropriate operational models for their target company types.
By applying the framework and metrics outlined in this article, investors can more effectively evaluate the operator function within venture studios and identify those positioned to deliver superior returns through systematic company building.
This article is part of a series of 10 articles formalizing and defining venture studios as an asset class. Together this articles form the foundational definitions of the venture studio model and provide a framework for comprehensive evaluation.
About the Author
Matthew Burris serves as the Senior Director of Research at the Venture Studio Forum, where his mission is to transition venture studios from an emerging asset class to an established asset class. In this role, he leads the creation of the rigorous data frameworks and due diligence standards required for institutional adoption.
This research is built upon the proprietary insights Matthew developed as Partner & Head of Insights at the 9Point8 Collective. By codifying the methodologies from his advisory work with corporate, university, economic development, and private studios, he provides the Forum with the foundational architecture needed to define the industry.
Connect with Matthew on LinkedIn.